M3FS (Make3FS) is a tool used to deploy, test and evaluate DeepSeek 3FS file system.
Preface
3FS is an all-flash file storage system that DeepSeek developed for AI training and inference. It has excellent performance. Right now, 3FS is open-source, but there are some challenges when it comes to deploying, testing, and evaluating it. Open3FS offers the open-source M3FS (Make 3FS) deployment tool. M3FS can deploy a 3FS cluster with 20 nodes in just 30 seconds and it works in non-RDMA environments too. Therefore, the difficulty of deployment is reduced.
Open3FS aims to offer users a free 3FS distribution to meet their immediate needs and enable them to quickly evaluate and test 3FS. Currently, the M3FS tool and 3FS container images are available on the Open3FS.com . The main features of M3FS are:
- Simplify the deployment process of 3FS clusters.
- Running 3FS component inside container.
- As many users’ virtual machine environments do not support RDMA, M3FS can use RXE to simulate RDMA.
In this article, we used servers supporting RDMA networks to deploy 3FS.
Of course, you can also use non-RDMA virtual machines for testing. M3FS supports deployment in non-RDMA environments.
Environmental Planning
We use 4 storage nodes and 4 client nodes. The network bandwidth of the servers is 50 Gbps and they support RDMA. Each storage node contains four local NVMe SSDs. If there is no NVMe SSD in the test environment, M3FS also supports using directories to act as NVMe SSDs to deploy a 3FS cluster. The servers uses Ubuntu 22.04 OS + Docker because containers will be used to run the 3FS software.
Node Hardware Configuration
The following table shows the configuration of storage and client nodes in our test environment:
| Node | IP | CPU | Memory | NVMe SSD | Network |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| open3fs-stor01 | 10.0.0.11 | 64 | 512 GiB | 4TB × 4 | 50 Gb RDMA |
| open3fs-stor02 | 10.0.0.12 | 64 | 512 GiB | 4TB × 4 | 50 Gb RDMA |
| open3fs-stor03 | 10.0.0.13 | 64 | 512 GiB | 4TB × 4 | 50 Gb RDMA |
| open3fs-stor04 | 10.0.0.14 | 64 | 512 GiB | 4TB × 4 | 50 Gb RDMA |
| open3fs-client01 | 10.0.0.101 | 96 | 256 GiB | - | 50 Gb RDMA |
| open3fs-client02 | 10.0.0.102 | 96 | 256 GiB | - | 50 Gb RDMA |
| open3fs-client03 | 10.0.0.103 | 96 | 256 GiB | - | 50 Gb RDMA |
| open3fs-client04 | 10.0.0.104 | 96 | 256 GiB | - | 50 Gb RDMA |
Network Topology and Configuration of 3FS Component Role
The role configuration of the 3FS component in this test is shown in the following figure. In actual production, at least three nodes should be configured for the mgmtd role.
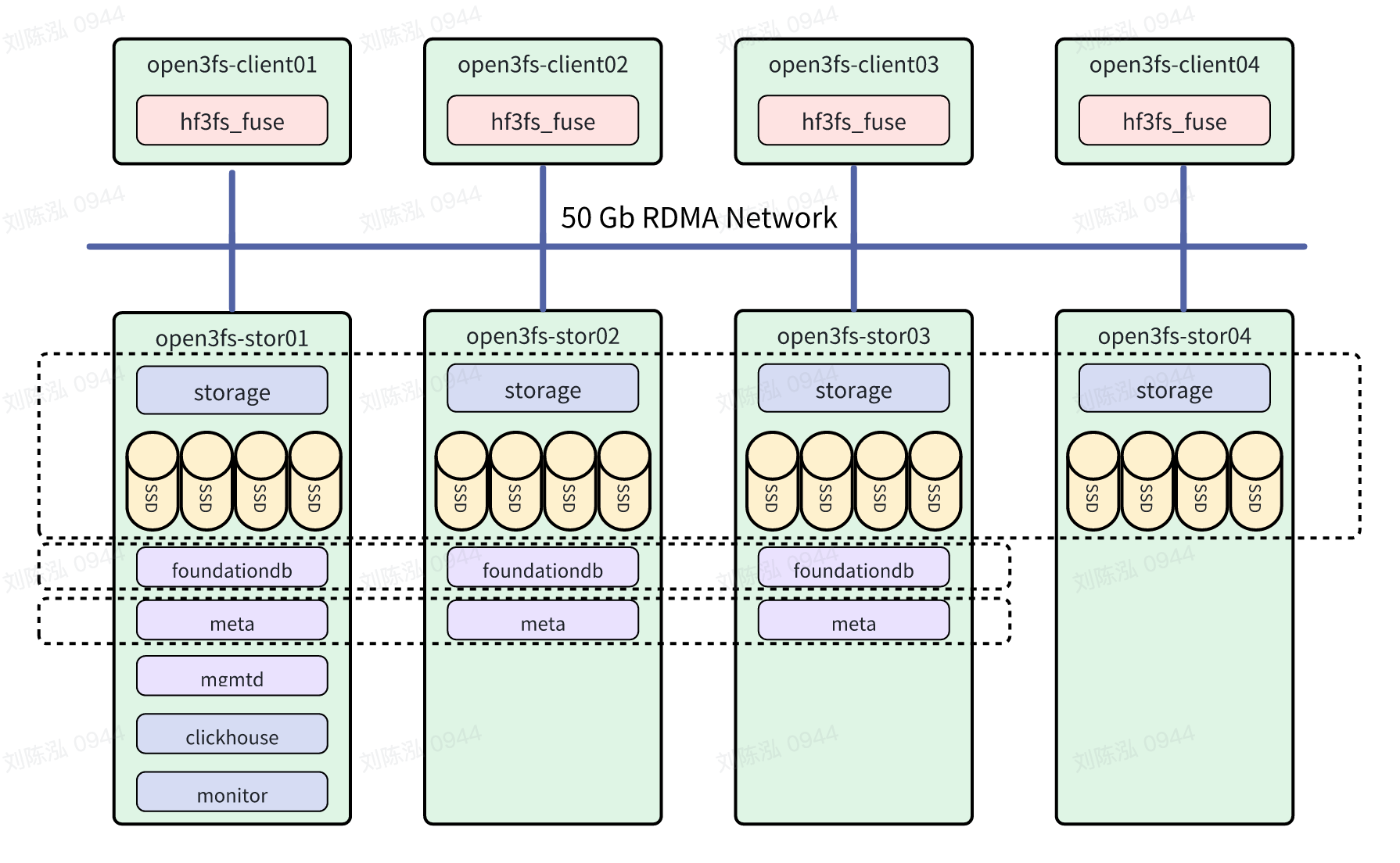
Node Configuration
Edit the /etc/hosts file on each node and add the following content.
10.0.0.11 open3fs-stor01
10.0.0.12 open3fs-stor02
10.0.0.13 open3fs-stor03
10.0.0.14 open3fs-stor04
10.0.0.101 open3fs-client01
10.0.0.102 open3fs-client02
10.0.0.103 open3fs-client03
10.0.0.104 open3fs-client04
When deploying 3FS, M3FS needs to use SSH to execute deployment operations on other nodes. Therefore, it is necessary to configure SSH Passwordless login access from the open3fs-stor01 node to all nodes.
All nodes need to install Docker CE.
Deploy a 3FS Cluster with M3FS
We use the open3fs-stor01 node as the main operating node during deployment.
One-step installation of m3fs
Install m3fs in one step on the open3fs-stor01 node.
curl -sfL https://artifactory.open3fs.com/m3fs/getm3fs | sh
Create and Edit the cluster.yml file
The 3FS file storage cluster includes component roles such as mgmtd, meta, monitor, fdb, clickhouse, storage, and hf3fs_fuse. It is necessary to specify on which nodes different roles are deployed in the cluster.yml file.
In addition, you can also configure the network type (supporting RDMA, ERDMA, and RXE, where RXE is a software-simulated RDMA), configure the hard disk type (supporting nvme and dir, where dir can be used in non-NVMe SSD environments), configure the number of replicas (the default value is 2, which means that the 3FS cluster can be deployed with at least 2 nodes), and configure the ChunkSize (the default is 1048576).
Execute the following command to generate the cluster.yml configuration file.
./m3fs config create
Edit the cluster.yml file. If you need to modify more configurations for 3FS cluster, please refer to https://github.com/open3fs/m3fs/blob/main/cluster.yml.sample.
name: "open3fs"
workDir: "/opt/3fs"
# networkType configure the network type of the cluster, can be one of the following:
# - RDMA: use RDMA network protocol
# - ERDMA: use aliyun ERDMA as RDMA network protocol
# - RXE: use linux rxe kernel module to mock RDMA network protocol
networkType: "ERDMA"
nodes:
- name: open3fs-stor01
host: "10.0.0.11"
username: "root"
- name: open3fs-stor02
host: "10.0.0.12"
username: "root"
- name: open3fs-stor03
host: "10.0.0.13"
username: "root"
- name: open3fs-stor04
host: "10.0.0.14"
username: "root"
- name: open3fs-client01
host: "10.0.0.101"
username: "root"
- name: open3fs-client02
host: "10.0.0.102"
username: "root"
- name: open3fs-client03
host: "10.0.0.103"
username: "root"
- name: open3fs-client04
host: "10.0.0.104"
username: "root"
services:
client:
nodes:
- open3fs-client01
- open3fs-client02
- open3fs-client03
- open3fs-client04
hostMountpoint: /mnt/3fs
storage:
nodes:
- open3fs-stor01
- open3fs-stor02
- open3fs-stor03
- open3fs-stor04
# diskType configure the disk type of the storage node to use, can be one of the following:
# - nvme: NVMe SSD
# - dir: use a directory on the filesystem
diskType: "nvme"
diskNumPerNode: 4
replicationFactor: 2
mgmtd:
nodes:
- open3fs-stor01
meta:
nodes:
- open3fs-stor01
- open3fs-stor02
- open3fs-stor03
monitor:
nodes:
- open3fs-stor01
fdb:
nodes:
- open3fs-stor01
- open3fs-stor02
- open3fs-stor03
clickhouse:
nodes:
- open3fs-stor01
images:
registry: ""
3fs:
repo: "open3fs/3fs"
tag: "20250315"
fdb:
repo: "open3fs/foundationdb"
tag: "7.3.63"
clickhouse:
repo: "open3fs/clickhouse"
tag: "25.1-jammy"
Download the 3FS container image
Execute the following command to download the container image of 3FS, with a total size of about 7GiB.
./m3fs artifact download -o 3fs_images -c cluster.yml
This command will download 3 container images to the /tmp/3fs/ directory and then package them into 1 file. If your network environment is poor, you can use other tools to download these 3 container images, copy them to the /tmp/3fs/ directory, and then execute the m3fs artifact download command.
https://artifactory.open3fs.com/3fs/3fs_20250315_amd64.docker
https://artifactory.open3fs.com/3fs/clickhouse_25.1-jammy_amd64.docker
https://artifactory.open3fs.com/3fs/foundationdb_7.3.63_amd64.docker
https://artifactory.open3fs.com/3fs/3fs_20250315_amd64.docker.sha256sum
https://artifactory.open3fs.com/3fs/clickhouse_25.1-jammy_amd64.docker.sha256sum
https://artifactory.open3fs.com/3fs/foundationdb_7.3.63_amd64.docker.sha256sum
Prepare the 3FS environment
The next command will distribute the 3FS container image to all nodes and automatically perform environment configuration. In a non-RDMA environment, RXE will be configured.
./m3fs cluster prepare -c cluster.yml -a 3fs_images
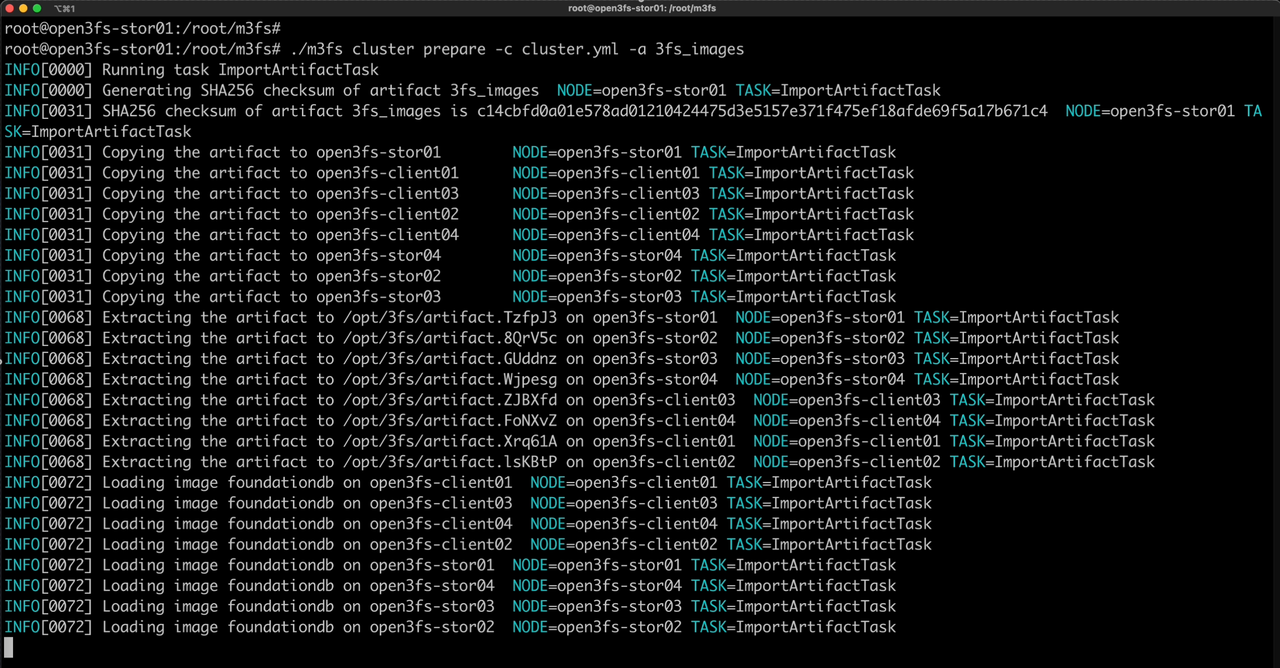
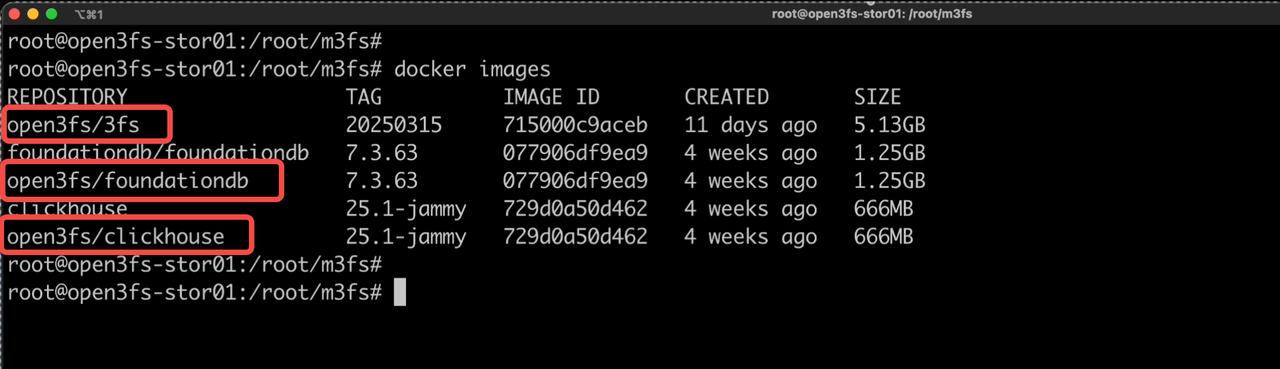
After executing the above commands, we can observe the newly added container images on the nodes.
One-step deploy the 3FS cluster
Finally, execute the following command to deploy the 3FS cluster within 30 seconds.
./m3fs cluster create -c ./cluster.yml
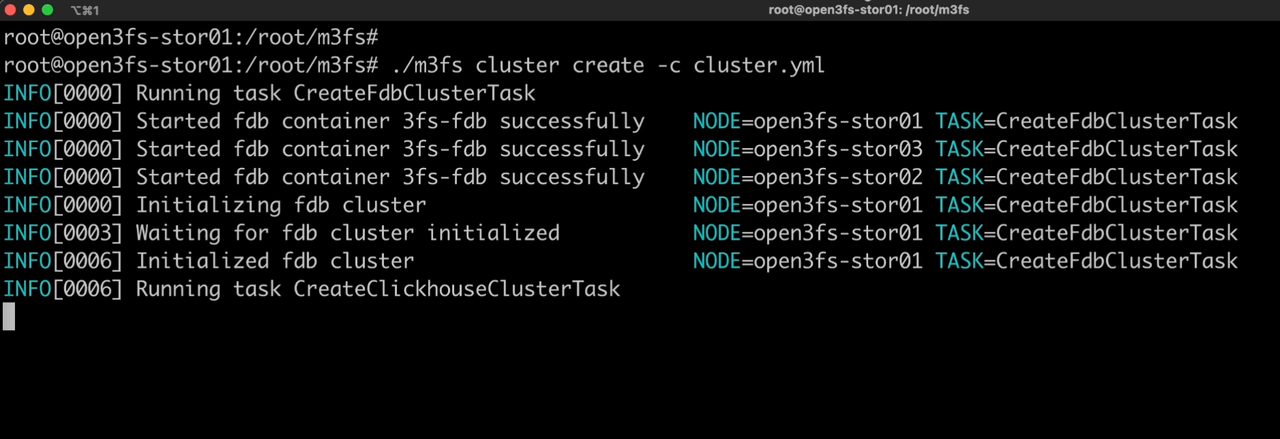
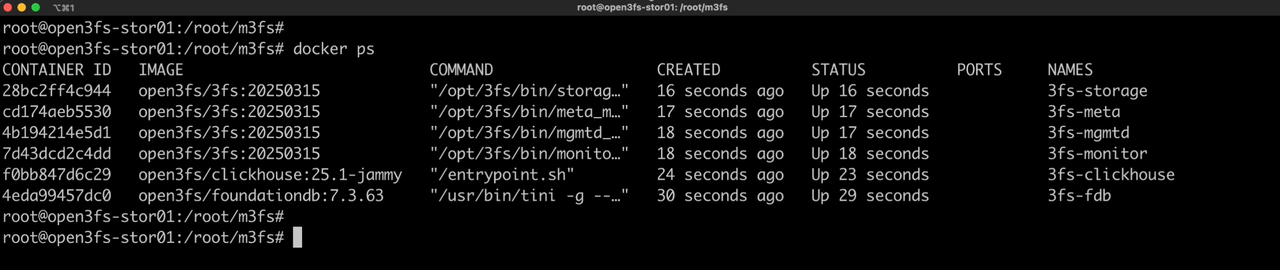
After m3fs successfully deploys a 3FS cluster, check the running status of the 3FS containers.
Check the 3FS cluster
After the 3FS cluster is deployed, we can execute the following command to check the list of 3FS roles.
/opt/3fs/admin_cli.sh "list-nodes"
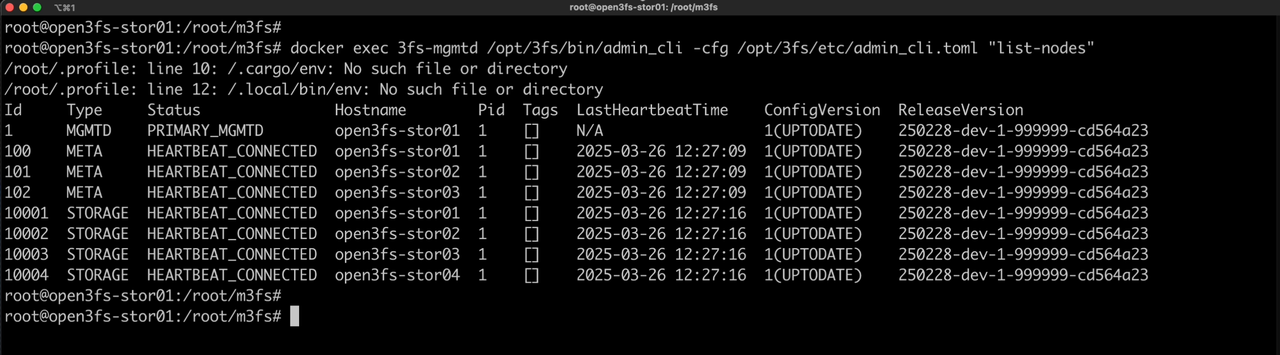
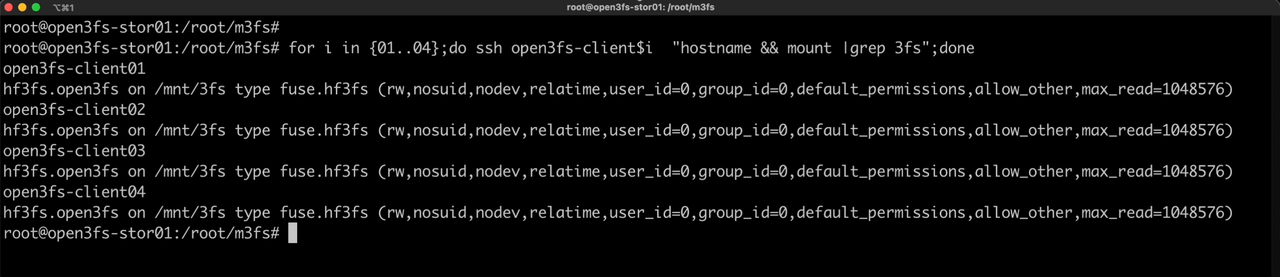
We can also check the status of the /mnt/3fs mount point on the client node.
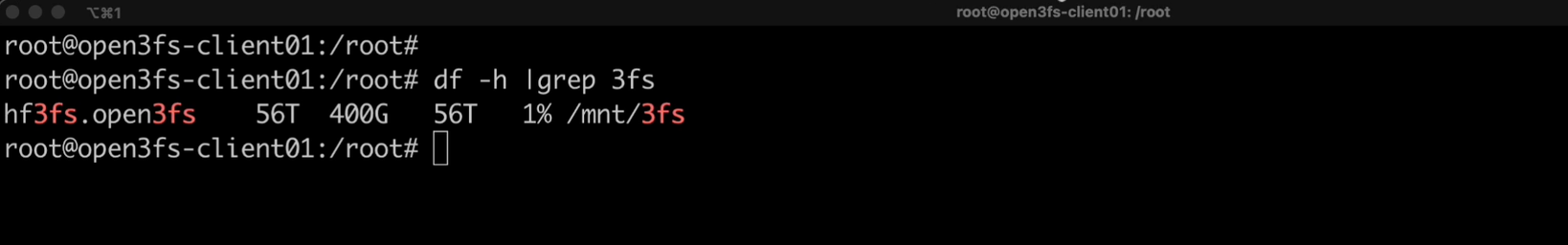
You can check the capacity statistics of 3FS file storage.
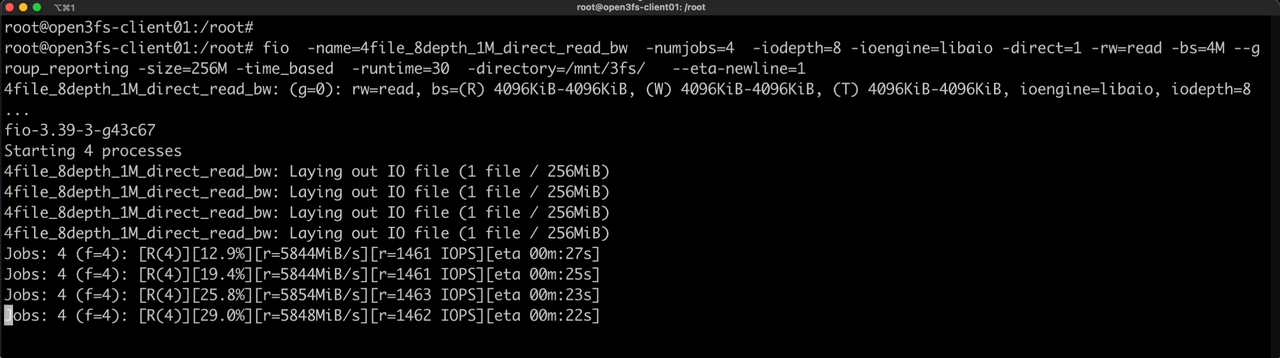
Use fio to perform performance testing on the 3FS cluster
Single-client testing using fio
Execute the following command on the terminal of the open3fs-client01 client node. This fio test is a 1MB sequential read test of four 256M files. According to the test results, the network bandwidth of a single client has been fully utilized.
fio -name=4file_8depth_1M_direct_read_bw -numjobs=4 -iodepth=8 -ioengine=libaio -direct=1 -rw=read -bs=4M --group_reporting -size=256M -time_based -runtime=30 -directory=/mnt/3fs/ --eta-newline=1
3FS Native User-space APIs
3FS provides a native user-space API interface, USRBIO, which can reduce multiple memory copies from the kernel space to the user space in traditional FUSE clients. Download the compressed package of the pre-compiled fio and hf3fs_usrbio.so files.
wget https://artifactory.open3fs.com/3fs/usrbio-fio-test.tar.gz
tar zxvf usrbio-fio-test.tar.gz
Extract the files to /root/usrbio-fio-test/
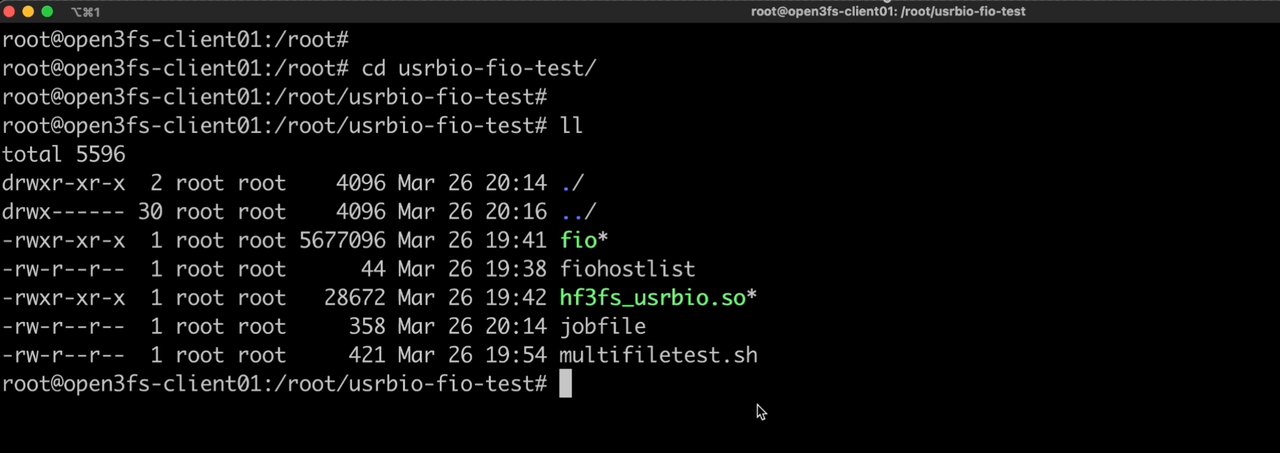
Single-client test using fio and hf3fs_usrbio
First, edit the jobfile.
[global]
iodepth=1
iodepth_batch_submit=1
iodepth_batch_complete_min=1
iodepth_batch_complete_max=1
numjobs=128
thread=1
size=256M
time_based
runtime=30
ramp_time=5
direct=1
directory=/mnt/3fs/
ioengine=external:/root/usrbio-fio-test/hf3fs_usrbio.so
group_reporting
name=usrbio-fio-test
[usrbio-fio-test]
bs=1M
rw=read
Execute the following command to test the 1MB sequential read performance of 128 files each with a size of 256MB on a single client. From the results, it can be seen that the network bandwidth of a single client has been fully utilized.
./fio jobfile --eta-newline=1
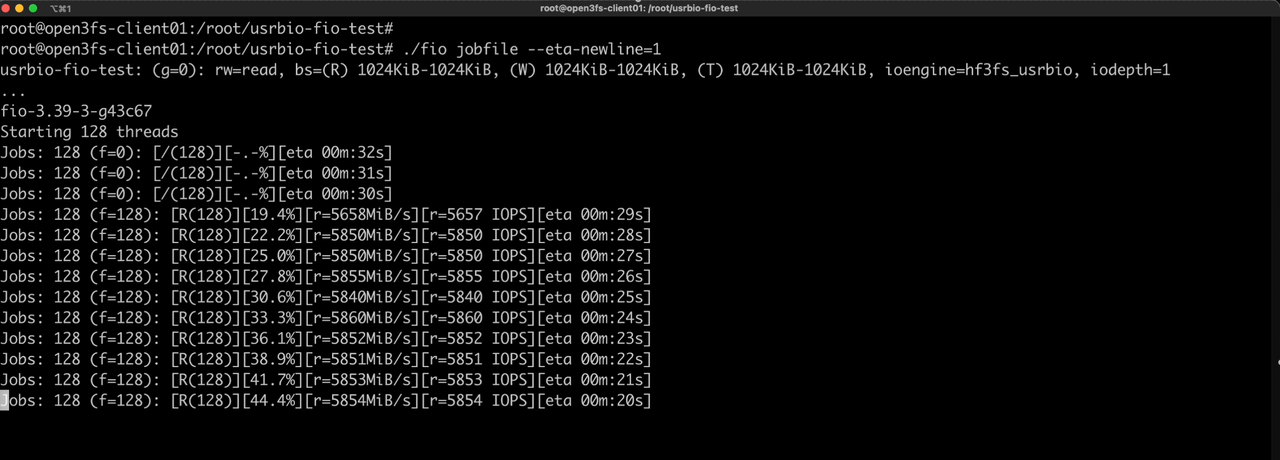
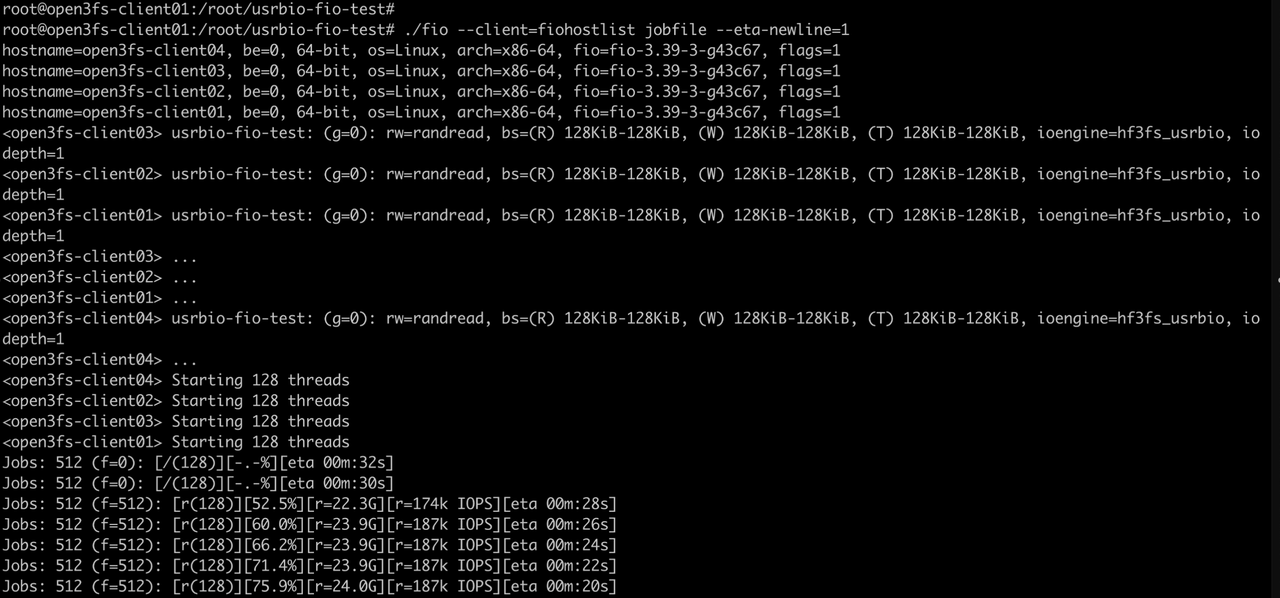
Multi-clients test using fio and hf3fs_usrbio.
Copy the /root/usrbio-fio-test/ directory to other client nodes, and then execute fio –server on each client node. We need to use the client/server mode of fio for multi-clients testing.
/root/usrbio-fio-test/fio --server &
Edit the hostlist file on the open3fs-client01 node and fill in the IP addresses of all client nodes.
10.0.0.101
10.0.0.102
10.0.0.103
10.0.0.104
Execute the multi-client test command on the open3fs-client01 node. From the results, it can be seen that the network bandwidth of 4 clients has been fully utilized.
./fio --client=fiohostlist jobfile --eta-newline=1
Performance result analysis
We did some performance tests with 4 clients and block sizes of 4KB, 128KB, and 1MB. Here are the results.
| Operation | numjobs | iodepth | IOPS | MiB/s | Lat(ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4KB randwrite | 128 | 1 | 14.7K | 57 | 34.72 |
| 4KB randread | 128 | 1 | 211K | 823 | 2.42 |
| 4KB randread | 128 | 1024 | 5,271K | 20,589 | 98.91 |
| 128KB randwrite | 128 | 1 | 14.6K | 1,825 | 35.10 |
| 128KB randread | 128 | 1 | 187K | 23,375 | 2.73 |
| 1MB write | 128 | 1 | 11.5K | 11,500 | 44.26 |
| 1MB read | 128 | 1 | 23.4K | 23,400 | 21.83 |
The test results show that the performance of 3FS is very good.
- The 4K random read IOPS of a single client can reach 1.3 million. The performance scales linearly with 4 clients, reaching 5.27 million IOPS and saturating the client network bandwidth.
- For single-client 1M sequential read, the speed can reach 5814MiB/s (limited by the 50Gb network bandwidth). When using 4 clients, the performance grows linearly, reaching 23,375 MiB/s and saturating the client network bandwidth.
Summary
With M3FS, we can quickly deploy 3FS in the x86 + Ubuntu 22.04 environment (supporting both physical machines and virtual machines, both RDMA and non-RDMA, and both with and without NVMe SSDs), which facilitates users to evaluate and test 3FS as soon as possible.
M3FS (Make 3FS) is written in Golang and used for the rapid deployment of 3FS clusters. The code repository is https://github.com/open3fs/m3fs.
Open3FS not only provides installation videos, container images, and deployment tools, but will also provide deployment guides, test reports, best practices, reference architectures and other content in the future to help more technology enthusiasts learn and use 3FS. Your feedback is highly anticipated.